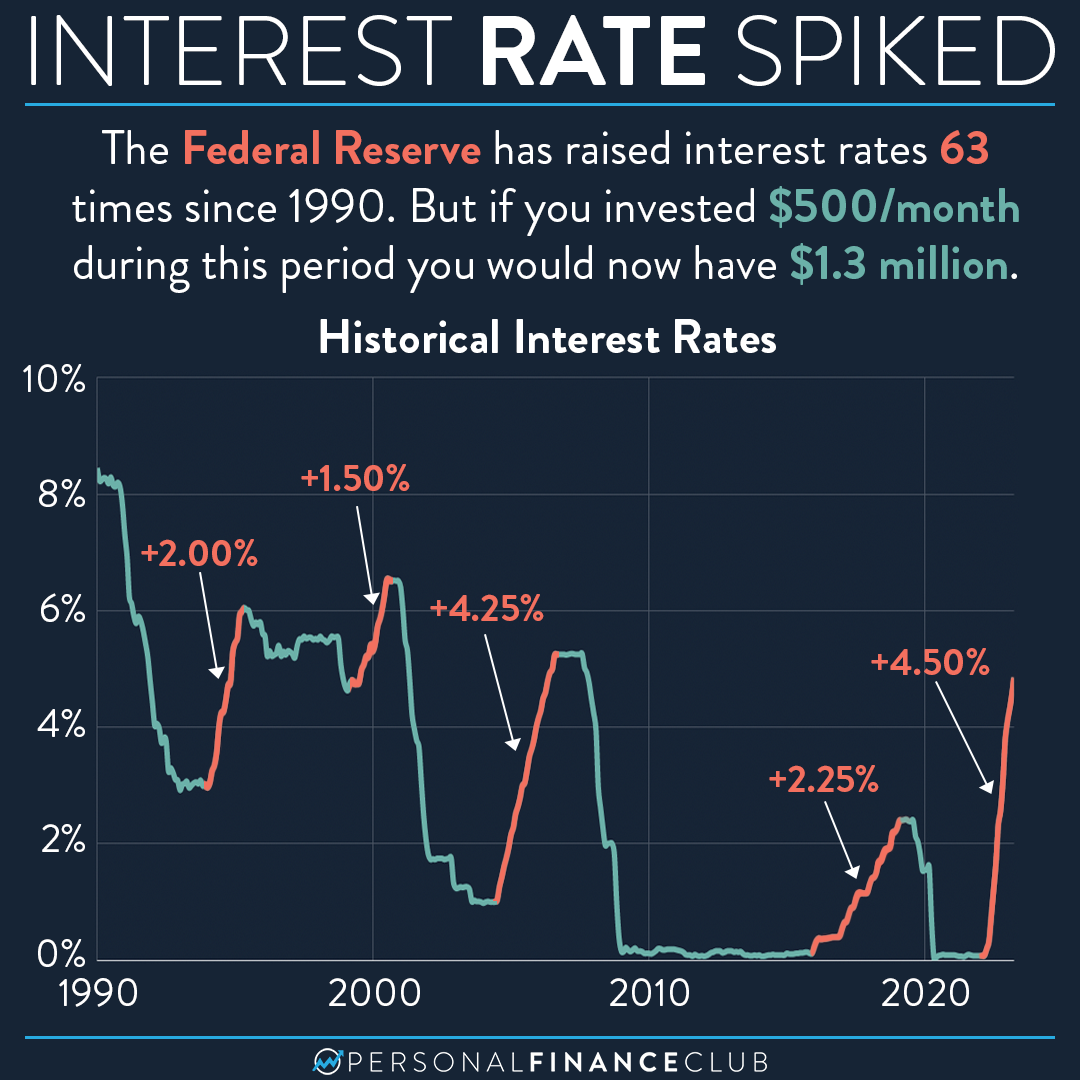
When it comes to federal reserve interest rates, there’s a lot more to the story than just numbers on a screen. It’s like the heartbeat of the economy—every tweak, every adjustment, sends ripples through the financial world. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or just someone trying to make sense of their savings account, understanding how the Federal Reserve manages interest rates can make all the difference. So, buckle up because we’re diving deep into this fascinating topic and uncovering what it means for your wallet.
Now, you might be thinking, "Why should I care about federal reserve interest rates?" Well, here's the deal: these rates influence everything from mortgage payments to credit card interest. They’re not just numbers floating around in some boardroom—they have real-world implications that affect your daily life. Think about it: when rates go up, borrowing gets more expensive, and when they drop, it becomes cheaper. That’s why staying informed is crucial.
As we journey through this article, we’ll break down the complexities of federal reserve interest rates in a way that’s easy to digest. We’ll cover everything from the basics of how the Federal Reserve works to the broader economic impacts of their decisions. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of why these rates matter and how you can use that knowledge to your advantage. Let’s get started!
Read also:Tara Beane The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment
Understanding the Federal Reserve: What It Is and Why It Matters
Before we dive headfirst into federal reserve interest rates, let’s take a step back and talk about the Federal Reserve itself. Established in 1913, the Fed, as it’s often called, is the central banking system of the United States. Its primary job? To keep the economy running smoothly. Sounds simple enough, right? But trust me, there’s a lot going on behind the scenes.
One of the Fed’s main responsibilities is managing monetary policy, which includes setting interest rates. This is done through the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), a group of policymakers who meet several times a year to decide on rate adjustments. Their goal is to strike a balance between encouraging economic growth and keeping inflation in check. It’s like walking a tightrope, and one wrong move could send the economy spiraling.
Here’s a fun fact: the Fed doesn’t just control interest rates; it also acts as the lender of last resort for banks. When banks run into trouble, the Fed steps in to provide liquidity, ensuring the financial system doesn’t collapse. So, while federal reserve interest rates are a big part of what the Fed does, they’re just one piece of a much larger puzzle.
How the Federal Reserve Sets Interest Rates
Alright, now that we know what the Federal Reserve is, let’s talk about how it sets those all-important interest rates. The process isn’t as straightforward as you might think. The FOMC uses a variety of economic indicators to guide its decisions, including employment data, inflation rates, and gross domestic product (GDP) growth.
When the economy is booming, the Fed might raise interest rates to prevent overheating and keep inflation under control. On the flip side, during a downturn, they might lower rates to stimulate borrowing and spending. It’s a delicate balancing act, and the Fed has to consider the long-term implications of each decision.
One tool the Fed uses to influence interest rates is open market operations. This involves buying and selling government securities to adjust the money supply. By increasing or decreasing the amount of money in circulation, the Fed can effectively control the cost of borrowing. It’s like turning a dial—each tweak has a ripple effect throughout the economy.
Read also:Mark Ramsey Age The Inside Story Youve Been Waiting For
The Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rates on the Economy
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s talk about the real-world impact of federal reserve interest rates. These rates don’t exist in a vacuum; they have far-reaching effects on everything from consumer spending to business investments. Understanding these dynamics is key to grasping why the Fed’s decisions matter so much.
For starters, when interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper. This encourages businesses to invest in new projects and consumers to take out loans for big-ticket items like homes and cars. Conversely, when rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can slow down economic activity. It’s a bit like adjusting the thermostat—turn it up, and things heat up; turn it down, and things cool off.
But it’s not just about borrowing. Federal reserve interest rates also influence the value of the dollar. When rates rise, foreign investors are more likely to park their money in U.S. assets, boosting the currency’s value. This can have both positive and negative effects, depending on the context. For example, a stronger dollar makes imports cheaper but can hurt exports by making them more expensive for foreign buyers.
How Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect Consumers
Let’s zoom in on the consumer side of things. For most people, federal reserve interest rates have a direct impact on their financial lives. Whether you’re saving for retirement, buying a house, or paying off credit card debt, these rates play a role in determining how much you’ll pay or earn.
Take mortgages, for instance. When interest rates are low, it’s a great time to buy a home because your monthly payments will be lower. But if rates rise, that same house could become much less affordable. The same goes for car loans, student loans, and even credit cards. Every time the Fed adjusts rates, it sends a signal to lenders, who then pass those changes on to consumers.
On the flip side, savers might not be too thrilled when rates are low. That’s because the return on savings accounts and certificates of deposit tends to decrease when borrowing costs are low. It’s a trade-off, and one that many people have to navigate when planning their finances.
Historical Context: How Federal Reserve Interest Rates Have Evolved
To truly understand the significance of federal reserve interest rates, it’s helpful to look at how they’ve evolved over time. The Fed’s approach to monetary policy hasn’t always been the same, and its decisions have been shaped by historical events and economic conditions.
For example, during the Great Depression, the Fed was criticized for not doing enough to stimulate the economy. In response, it adopted a more proactive stance, using interest rates as a tool to manage economic cycles. Fast forward to the 1970s, and we see a different story. High inflation forced the Fed to raise interest rates sharply, leading to a recession but ultimately bringing inflation under control.
More recently, the 2008 financial crisis saw the Fed slash interest rates to near zero in an effort to stabilize the economy. This period of ultra-low rates lasted for years, fueling a recovery but also raising concerns about asset bubbles. As the economy healed, the Fed gradually began raising rates again, only to lower them once more in response to the pandemic.
Key Moments in Federal Reserve Interest Rate History
- 1980s: The Volcker Era – Paul Volcker, then Fed Chair, raised interest rates to unprecedented levels to combat soaring inflation. It worked, but at the cost of a deep recession.
- 2000s: The Housing Bubble – Low interest rates contributed to a boom in housing prices, setting the stage for the 2008 financial crisis.
- 2020s: Pandemic Response – In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed slashed rates to near zero, injecting liquidity into the economy and supporting recovery efforts.
Each of these moments highlights the Fed’s role in shaping the economic landscape. By learning from the past, we can better understand the decisions being made today and their potential consequences for the future.
How Federal Reserve Interest Rates Affect Businesses
Businesses, both big and small, are heavily influenced by federal reserve interest rates. For startups and small businesses, access to affordable credit can mean the difference between success and failure. When rates are low, it’s easier to secure loans for expansion, inventory, or hiring. But when rates rise, borrowing costs go up, which can put a strain on cash flow.
Large corporations also feel the impact, though they often have more resources to weather the storm. Higher interest rates can lead to reduced investment in new projects, as the cost of capital increases. This, in turn, can slow down job creation and economic growth. It’s a domino effect, and the Fed has to carefully weigh the potential consequences of its actions.
Another factor to consider is the global impact of federal reserve interest rates. U.S. businesses operating internationally may find themselves at a disadvantage if the dollar strengthens due to rate hikes. This can affect everything from pricing strategies to competitiveness in foreign markets.
Strategies for Businesses to Navigate Interest Rate Changes
So, what can businesses do to prepare for fluctuations in federal reserve interest rates? Here are a few strategies:
- Lock in Rates – If you anticipate rates rising, consider locking in a fixed rate on loans or mortgages.
- Optimize Cash Flow – Keep a close eye on expenses and cash flow to ensure you can weather any increases in borrowing costs.
- Diversify Funding Sources – Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Explore alternative funding options to reduce reliance on traditional loans.
By taking proactive steps, businesses can mitigate the risks associated with interest rate changes and position themselves for long-term success.
Global Implications of Federal Reserve Interest Rates
While federal reserve interest rates primarily affect the U.S. economy, their impact extends far beyond American borders. In today’s interconnected world, monetary policy decisions made by the Fed can have ripple effects across the globe. Emerging markets, in particular, are often vulnerable to changes in U.S. interest rates.
When the Fed raises rates, capital tends to flow back to the U.S. in search of higher returns. This can lead to currency depreciation and financial instability in developing countries. Conversely, when rates are low, emerging markets may benefit from increased investment flows, but they also face the risk of overheating if too much money floods in too quickly.
For global investors, understanding federal reserve interest rates is crucial. It helps them anticipate market movements and make informed decisions about where to allocate their resources. Whether you’re managing a portfolio or simply following the news, staying up-to-date on the Fed’s actions can give you a competitive edge.
How Countries Respond to Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes
Different countries have different strategies for dealing with the impact of federal reserve interest rates. Some may choose to raise their own rates to attract capital, while others may opt for currency interventions to stabilize their exchange rates. It’s a complex dance, and each nation must weigh the pros and cons based on its unique economic situation.
One thing is certain: the Fed’s decisions have global implications, and understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone interested in international finance. By keeping an eye on both domestic and international developments, you can better navigate the ever-changing economic landscape.
Future Trends in Federal Reserve Interest Rates
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the trajectory of federal reserve interest rates. One of the biggest factors is the ongoing battle against inflation. With prices rising at their fastest pace in decades, the Fed faces pressure to tighten monetary policy without stifling economic growth. It’s a tricky balancing act, and one that will likely dominate the headlines in the coming years.
Another trend to watch is the role of technology in influencing monetary policy. Advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence are giving the Fed new tools to monitor economic conditions in real time. This could lead to more precise and timely adjustments to interest rates, potentially reducing the volatility we’ve seen in the past.
Finally, the global shift toward sustainability is likely to impact federal reserve interest rates. As governments and businesses prioritize environmental goals, the Fed may find itself under pressure to align its policies with these objectives. This could lead to new approaches to monetary policy that take into account not just economic factors, but also social and environmental considerations.
What to Expect in the Next Decade
Looking ahead, here are a few things to keep an eye on:
- Inflation Management – The Fed will continue to focus on controlling inflation while supporting economic growth.
- Technological Innovation – Advances in data analytics and AI will enhance the Fed’s ability to make informed decisions.
- Sustainability – Expect increasing pressure for the Fed to incorporate environmental and social factors into its policy framework.
By staying informed about these trends, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Conclusion: Why Federal Reserve Interest Rates Matter to You
So, there you have it—a deep dive into the world of federal reserve interest rates. From their role in shaping the economy to their impact on your personal finances, these rates are a critical piece of the financial puzzle. Whether you’re a consumer, a business owner, or an investor, understanding how the Fed manages interest rates can help you make smarter decisions and achieve your financial goals.
As we’ve seen, the Fed’s decisions don’t exist in a vacuum. They’re influenced by a wide range of factors, from domestic economic conditions to global market dynamics. By staying informed and adapting